Hrct Interstitial Lung Disease
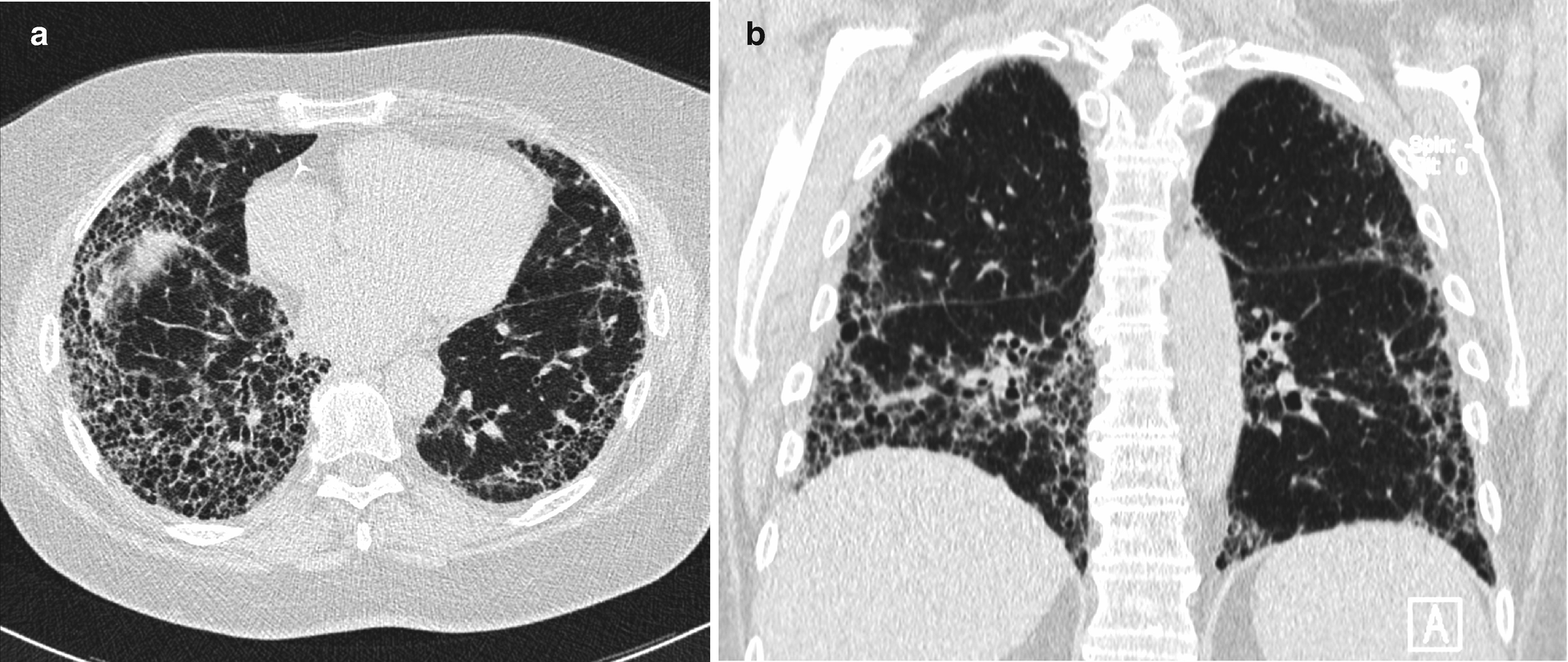
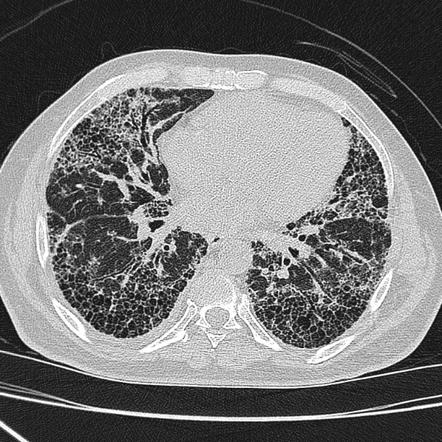
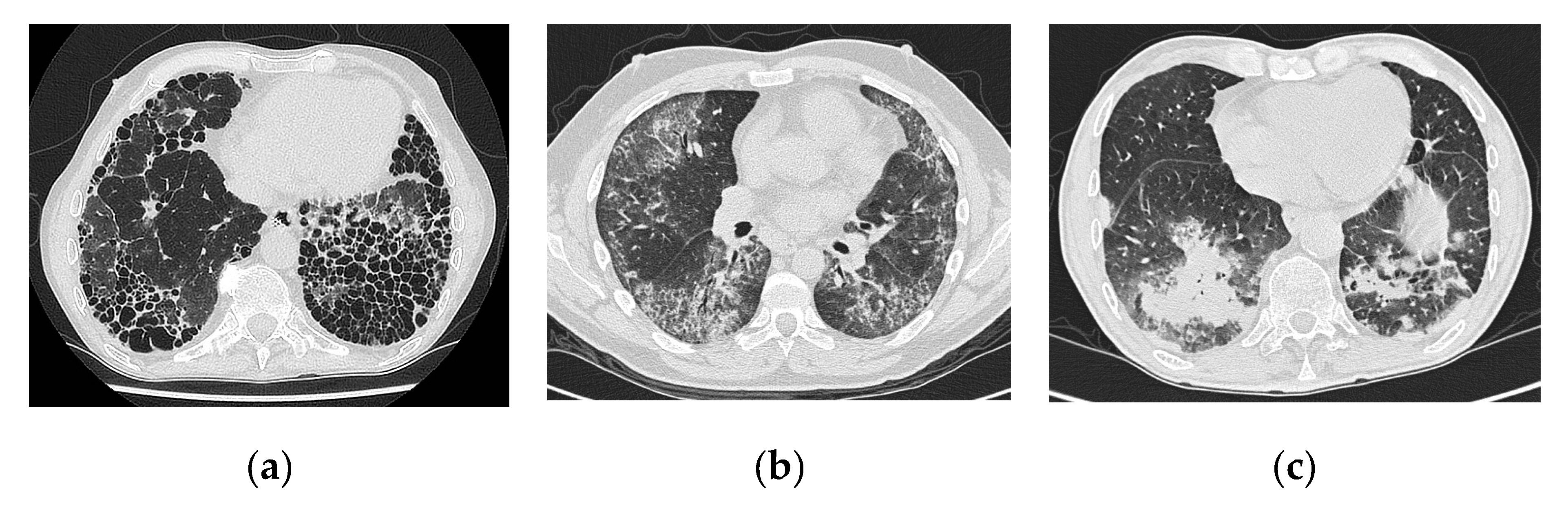
Hrct interstitial lung disease. Encontre diversos livros escritos por Kocova Eva com ótimos preços. Within this classification each disorder is introduced using a specific case with detailed information on patient history course of the illness and laboratory and pulmonary function tests. In areas of fibrosis there will be characteristic honeycombing.
He had a 30-pack-year smoking history. Approximately 60 to 70 of patients with sarcoidosis have characteristic radiologic findings. IPF is a chronic progressive fibrosing interstitial lung disease associated with a histologic andor HRCT pattern of usual interstitial pneumonia UIP 23.
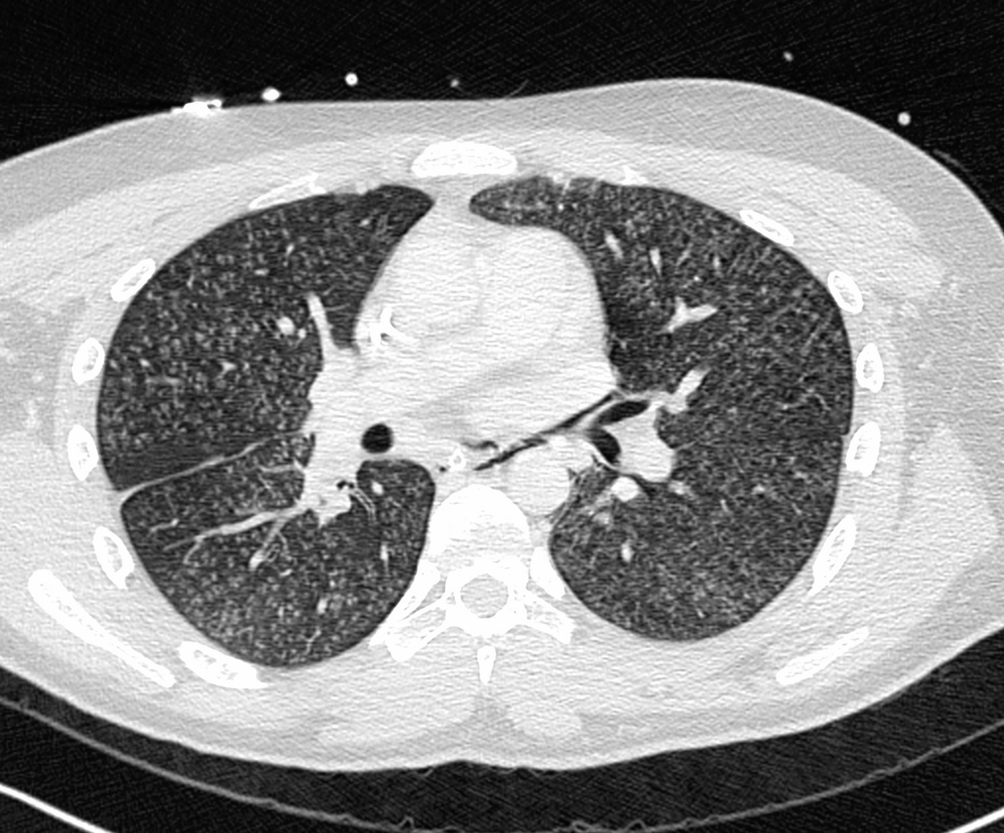
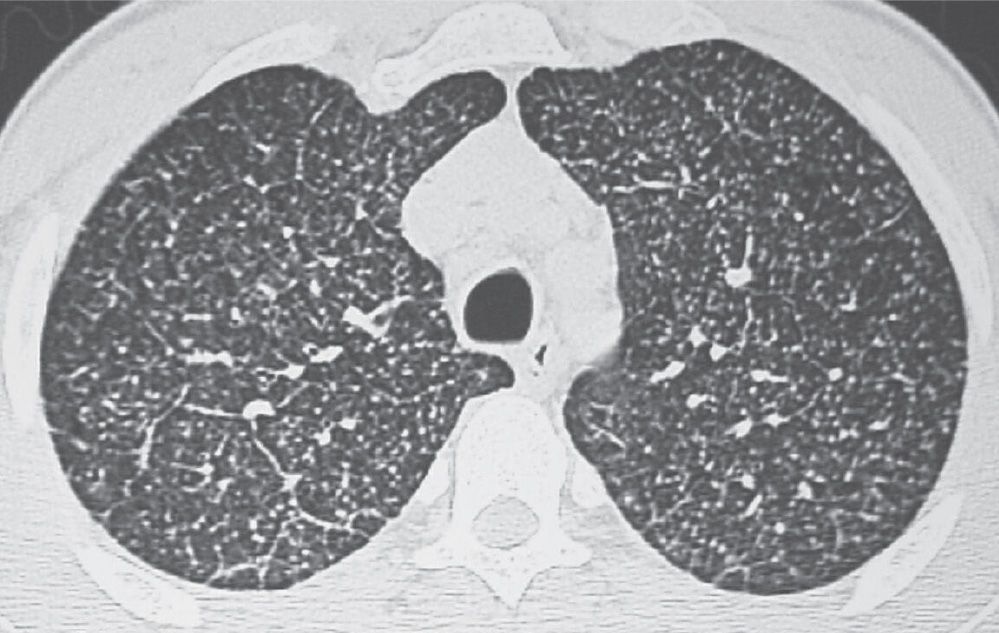
The advent of HRCT and the development of advanced reconstruction algorithms has allowed confident diagnoses of interstitial lung disease without surgical lung biopsy a significant advancement as lung biopsy confers additional risk. The interpretation of interstitial lung diseases is based on the type of involvement of the secondary lobule. Low attenuation linear opacities nodular and high attenuation.
Knowledge of the lung anatomy is essential for understanding HRCT. The differential diagnosis of HRCTs is based on the analysis of the predominant CT pattern the ancillary CT findings and the distribution of the findings. HRCT plays a central role in the differential diagnosis of interstitial lung diseases.
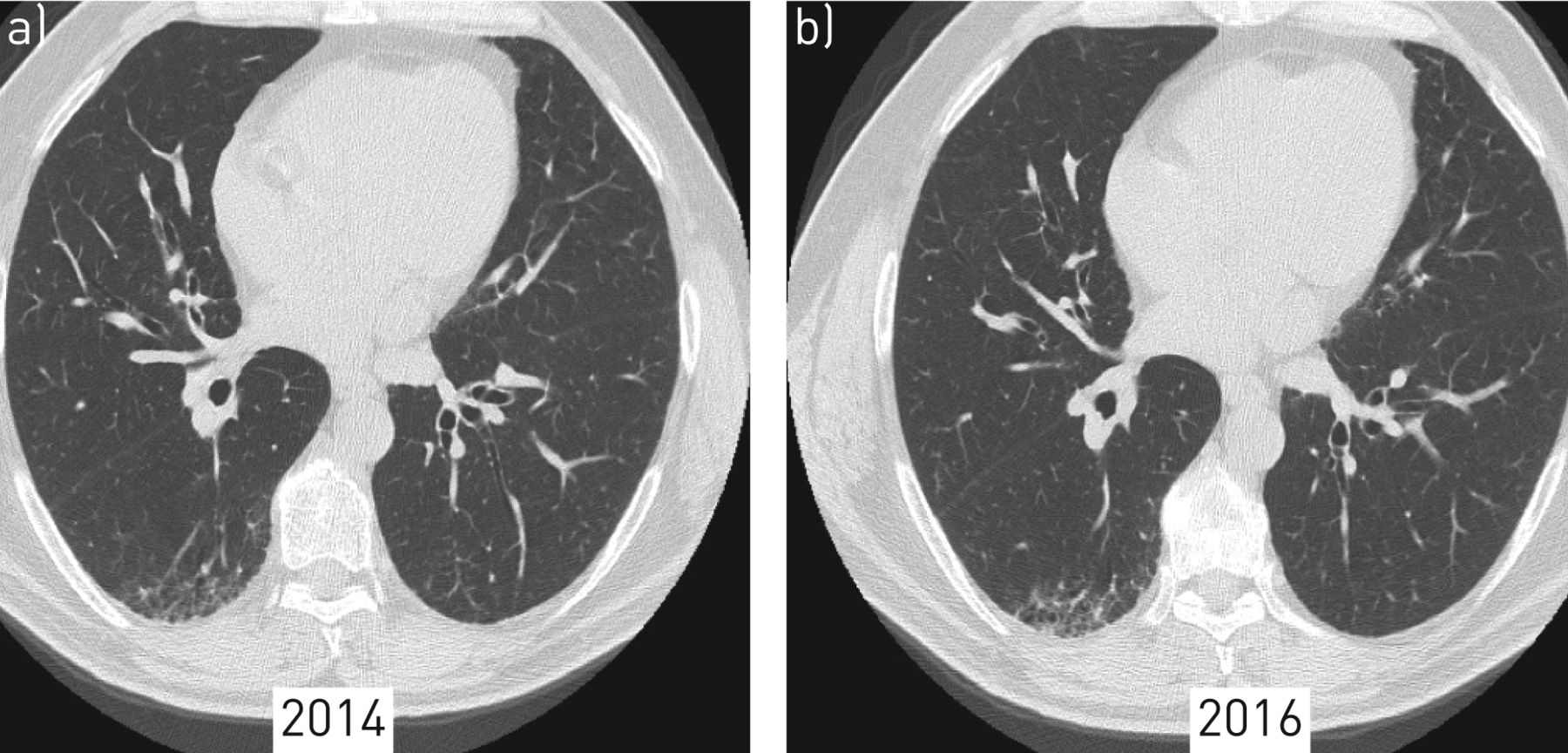
HRCT in smoking-related interstitial lung diseases. Although the position of HRCT as the dominant imaging technique for interstitial lung disease has remained unchallenged since its introduction in the late 1980s the roles assumed by HRCT have undergone a. The differential diagnosis of HRCTs is based on the analysis of the predominant CT pattern the ancillary CT findings and the distribution of the findings.
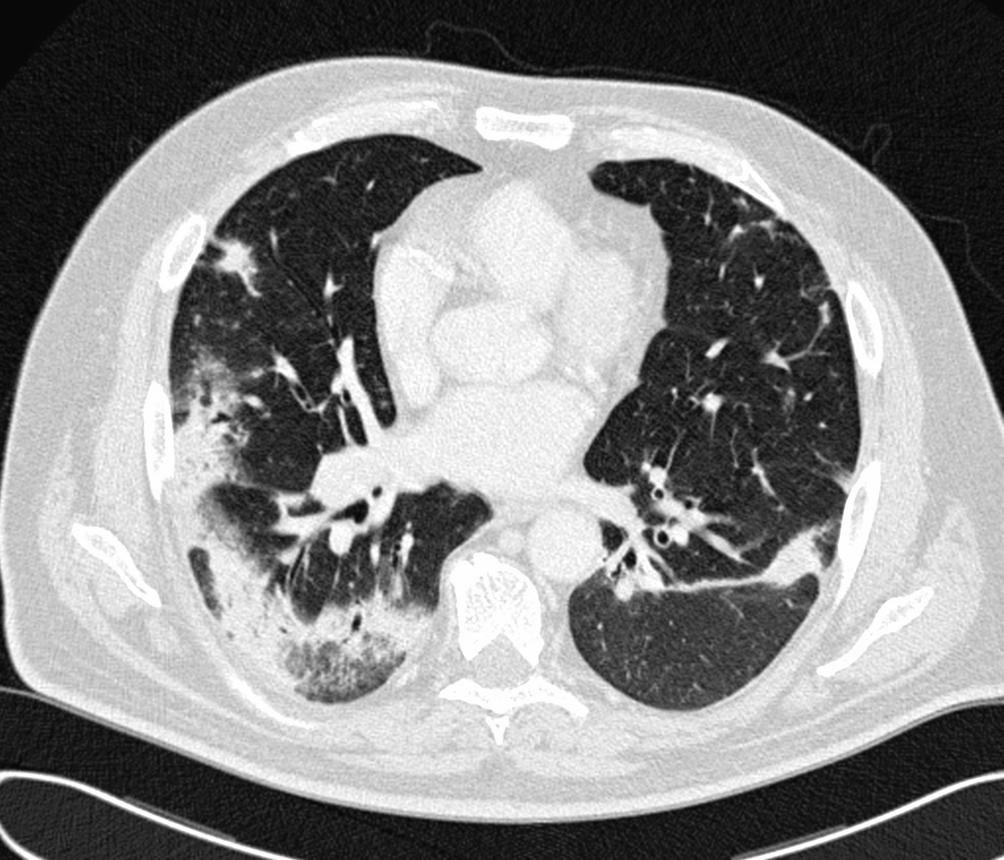
In 25 to 30 of cases the radiologic findings are atypical. At low-power microscopy there is temporally heterogeneous fibrosis admixed with areas of unaffected lung 2. Respiratory bronchiolitisinterstitial lung disease.
The final diagnosis of DILDs requires a combination of radiological clinical and sometimes pathological. Instructive Case Studies de Kocova Eva na Amazon.
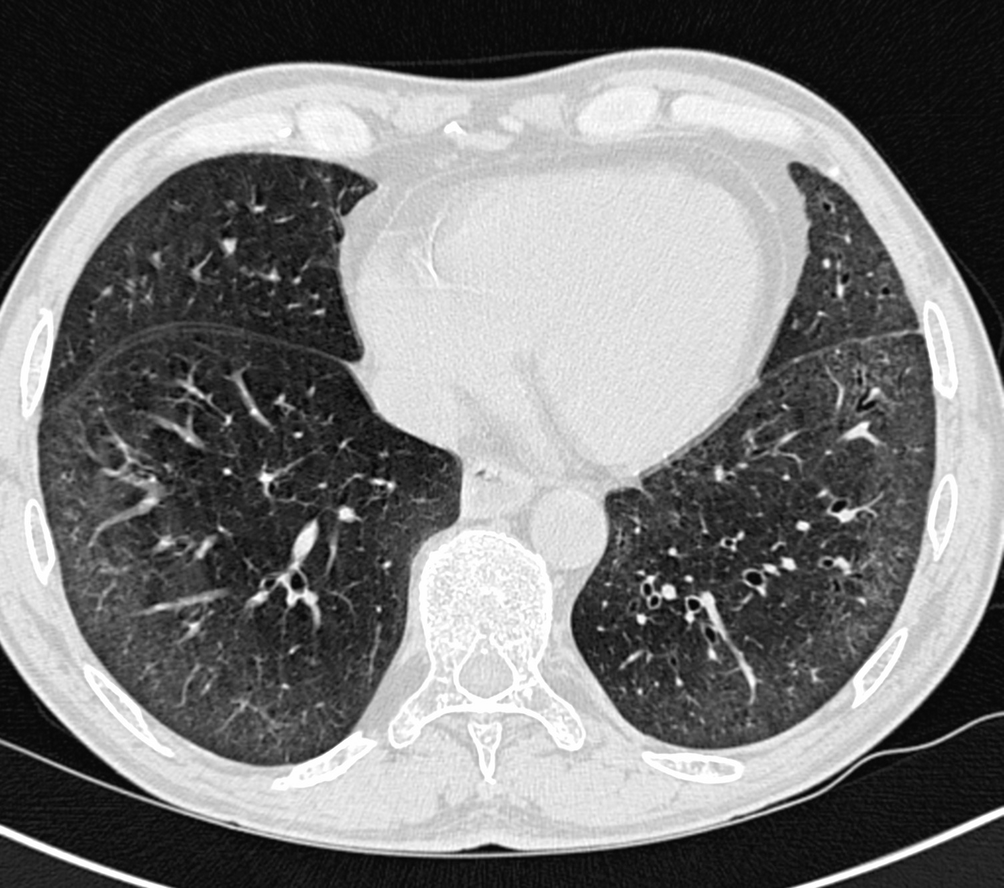
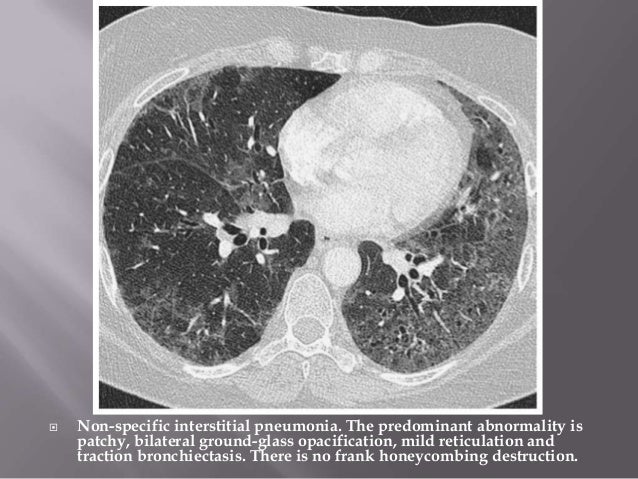
Several areas of non-specific ground-glass opacification in the right middle lobe and both lower lobes 29.
The second part is organized according to the four dominant types of HRCT pattern encountered in interstitial lung disease. Although the position of HRCT as the dominant imaging technique for interstitial lung disease has remained unchallenged since its introduction in the late 1980s the roles assumed by HRCT have undergone a. Approximately 60 to 70 of patients with sarcoidosis have characteristic radiologic findings. Low attenuation linear opacities nodular and high attenuation. Several different high resolution computed tomography HRCT patterns related to pulmonary drug toxicity have been reported in literature and the most frequent ILDs patterns reported include Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia NSIP Usual Interstitial Pneumonia UIP Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis HP Organizing Pneumonia OP Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome ARDS and Diffuse Alveolar. The final diagnosis of DILDs requires a combination of radiological clinical and sometimes pathological. HRCT plays a central role in the differential diagnosis of interstitial lung diseases. It is the smallest lung unit that is surrounded by connective tissue septa. The HRCT appearance of pulmonary sarcoidosis varies greatly and is known to mimic many other diffuse infiltrative lung diseases.
The peripheral interstitium subpleural interstitium surrounds the surface of the lung beneath the visceral pleura and penetrates the lung to surround the pulmonary lobules paraseptal interstitium. The second part is organized according to the four dominant types of HRCT pattern encountered in interstitial lung disease. Low attenuation linear opacities nodular and high attenuation. The peripheral interstitium subpleural interstitium surrounds the surface of the lung beneath the visceral pleura and penetrates the lung to surround the pulmonary lobules paraseptal interstitium. He had a 30-pack-year smoking history. The final diagnosis of DILDs requires a combination of radiological clinical and sometimes pathological. Several different high resolution computed tomography HRCT patterns related to pulmonary drug toxicity have been reported in literature and the most frequent ILDs patterns reported include Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia NSIP Usual Interstitial Pneumonia UIP Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis HP Organizing Pneumonia OP Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome ARDS and Diffuse Alveolar.






























Posting Komentar untuk "Hrct Interstitial Lung Disease"